Catalase test
General information
Many aerobic bacteria and most of those which are facultatively anaerobic produce the enzyme catalase. The function of this enzyme is to detoxify hydrogenperoxide (H2O2), which is formed from the superoxide radical by superoxide dismutase. Many aerotolerant anaerobic bacteria have peroxidase (which is not the same enzyme as cytochrome c oxidase) instead of catalase. Obligate anaerobic bacteria lack superoxide dismutase and catalase.
Catalase contains a heme group at the active site and it is catalyzing the following reaction with a very high turnover number:
2 H2O2 → 2 H2O + O2
Method
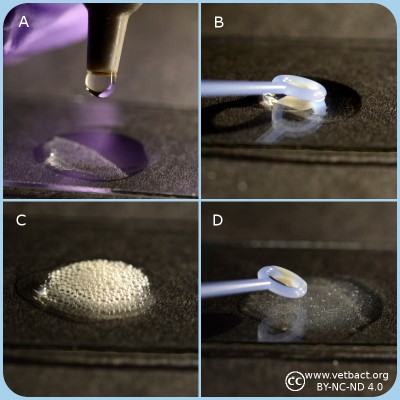
- Spread the bacteria on an agar plate and inkubate the plate over night (18-24 h) under appropriate conditions.
- Collect bacteria from one colony with a sterile inoculating loop (of plastic or platinum) and apply the bacteria on a microscope slide.
- If the bacteria are collected from a blood agar plate, one has to avoid contamination of agar, because hemoglobin also contains heme groups which can cause a false positive reaction.
- Add one drop of 3% H2O2 to the bacteria and observe the suspension. Be careful with the handling of H2O2 which is corrosive!!!
- Positive test resultat: Gas formation (O2) in the form av bubbles shows that the bacterium has a catalase.
- Negative test resultat: No gas formation.
Applications
The catalse test is primarily used for gram positive bacteria and can for instance be utilized to distinguish Staphylococcus spp. and Micrococcus spp., which are catalase positive from Streptococcus spp. and Enterococcus spp., respectively, which are catalase negative.
Updated: 2017-12-20.
|